go to WEEK 12 Online Course Support
MSE 5090: Case Studies in Material Selection
Week 12 - Midterm Problems
- Identify Process Routes
- Identify Candiate Materials
- Copper vs Steel Nails
- First Order Differences
- Midterm Solutions

MSE 5090 Midterm Test
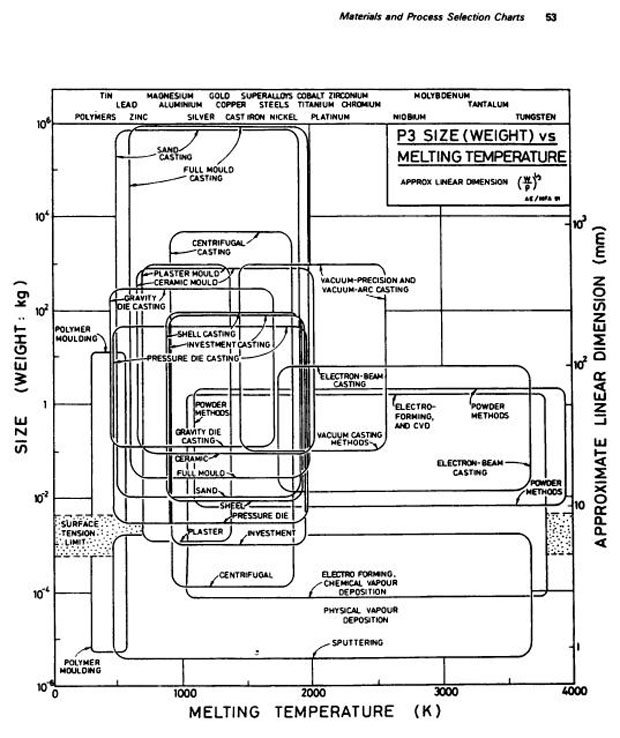
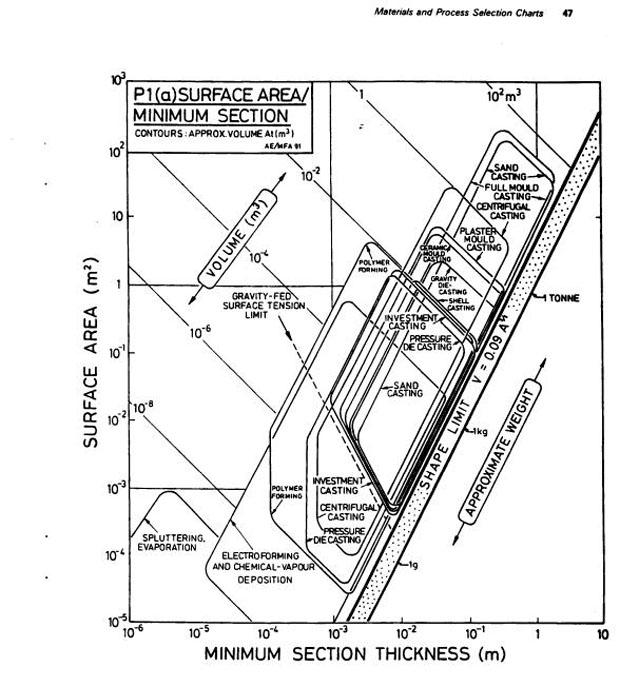
(Nov. 9, 1998)Identify Process Routes for electron microscopy grids
1. Small grids of copper (melting point = 1360K;density = 8.96 Mg/M3) are required to support samples for electron microscopy. The grids are circular disks, 8 mm in diameter and 1 mm thick, Use attached Charts P1(a) and P3 to identify possible process routes. (30 points)

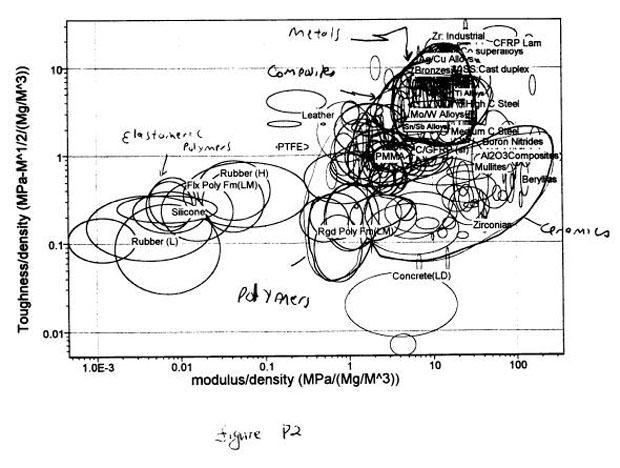
Identify Candiate Materials for an overconstrained tie rod
2. A tie, of length I and cross section area A, loaded in tension, is to support a load F, at minimum weight, without fracturing (the first constraint) or extending elastically by more than 6max (the second constraint). Use attached Figure P2 to identify three top
candidate materials for the tie when:
Useful solutions: The applied stress may be written as For Fracture one can write the constraint that For stiffness, the constraint may be written as Goto Problem 2 Solution

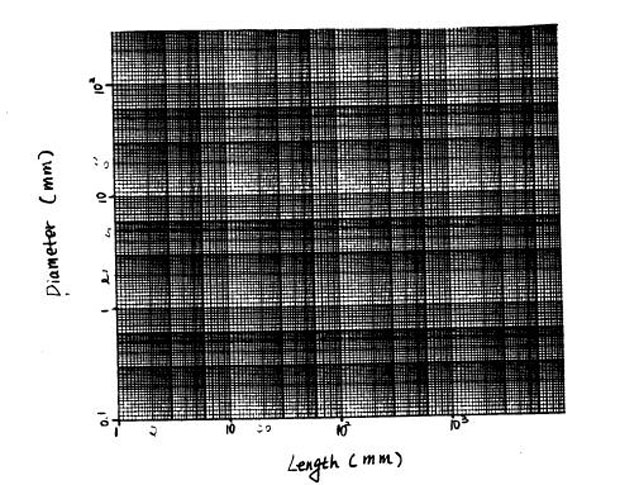
Scaling of Copper vs Steel Nails3. Nails come in a range of sizes. For example, a steel nail with a diameter of 5mm could have a maximum length up to 150 mm. (30 points)
(a) Develop a model for the design of nails, assuming that the length, for a given diameter, is limited by elastic buckling, and the force required to drive a nail into wood is proportional to the square of the diameter. Use your model to predict the maximum length of a steel nail with a diameter of 1 mm. (15 points)
(b) Graph your answer on the attached diameter vs. length (log-log) chart, and determine the slope of the line for the steel nails. Hint, use nails of length 150mm and the max length from A above. (5 points)
(c) Use your model to determine the diameters of two copper nails with the same lengths as the steel nails (the example and your answer for part (a)). (5 points)
(d) Plot the diameter vs. length for the copper nails on the chart and explore whether
your model will account accurately for the separation of the lines describing copper and
steel nails. (5 points)(Young's modulus, E, for steel, is 225 GPa; for copper it is 144 GPa)